LADICIM Leads the Cantabrian Project Applying AI to Reduce Emissions in Industry, Energy, and Transport
The INTELEST project, funded by the Government of Cantabria with European funds, involves the collaboration of companies such as GSW and Rocacero, research centers like IHCantabria, and industry organizations such as MAFEX.
Climate change, driven by the increase in greenhouse gases due to human activity, is causing global warming, climate disruptions, polar ice melt, sea level rise, and more frequent and severe extreme weather events. These phenomena have adverse effects on ecosystems, biodiversity, food security, water resources, and human health, posing a major challenge to sustainable development and global well-being.
The INTELEST project, led by the Laboratory of Materials Science and Engineering (LADICIM) at the University of Cantabria, aims to develop various Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tools to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in strategic sectors such as transport, energy, and industry. The ultimate goal of the project is to transfer the generated scientific and technological knowledge to the regional industrial and productive fabric—particularly in Cantabria—by optimizing industrial processes, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation practices, thereby making a meaningful contribution to the global fight against climate change.
INTELEST is funded by the Cantabrian Government’s Department of Industry through the FEDER 2021–2027 program, under the call “Aid Program for High-Industrial-Potential Research Projects by Technological Excellence Agents for Industrial Competitiveness (TCNIC).”
“The project is part of a knowledge transfer strategy aimed at directly benefiting Cantabria’s productive and industrial sector by providing advanced tools to address the challenges of climate change,” explains Professor Emeritus Federico Gutiérrez-Solana, project coordinator. “All of this is achieved through the adaptation and application of knowledge generated over nearly four decades of research at LADICIM, combined with the implementation of cutting-edge technologies in the modeling and optimization of industrial processes, transport infrastructures, and energy generation systems.”
A Project with Four Research Areas
INTELEST is built on a key premise: Artificial Intelligence offers a powerful set of tools with transformative potential, capable of delivering innovative solutions to complex, multifaceted problems such as climate change. To focus that potential, the project selected the strategic sectors of industry, energy, and transport—not only because of their significant contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions, but also due to their potential for adopting more sustainable and efficient practices.
By targeting these three distinct sectors, the INTELEST project is structured into four research areas in which LADICIM has extensive expertise and knowledge. In just the past five years, various researchers from the Laboratory have published over 100 articles indexed in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) related to these four lines of work.

“The Laboratory has experience applying AI tools in some of its research areas, but INTELEST marks a turning point in this regard, as it involves the widespread application of AI across all our lines of work,” explains Professor Emeritus Gutiérrez-Solana, founder of the Laboratory over 40 years ago. “Our research is highly focused on knowledge transfer, particularly within engineering fields such as transport and energy, and integrating AI into all our activities will further enhance our ability to serve industry. At the same time, INTELEST will allow us to generate a broader positive impact by facilitating reductions in energy consumption and emissions. This will not only improve the competitiveness of Cantabrian companies—it will also help in the fight against climate change.”
Line 1: Optimization of Energy Consumption in Steel Production
The first line of work within the INTELEST project builds on the long-standing collaboration between LADICIM and Global Steel Wire (GSW), a European leader in the production of high-value-added steel and one of the main industrial centers located in Cantabria. This ongoing partnership has always focused on reducing energy consumption in industrial processes—a strategic goal for GSW.
INTELEST will mark a significant step forward in this collaboration between academia and industry. Using advanced numerical simulation tools and machine learning algorithms, a team led by LADICIM professor Diego Ferreño will develop a digital twin of the induction furnace used in the steel billet manufacturing process. The objective is to optimize the furnace’s operation and reduce its energy consumption.
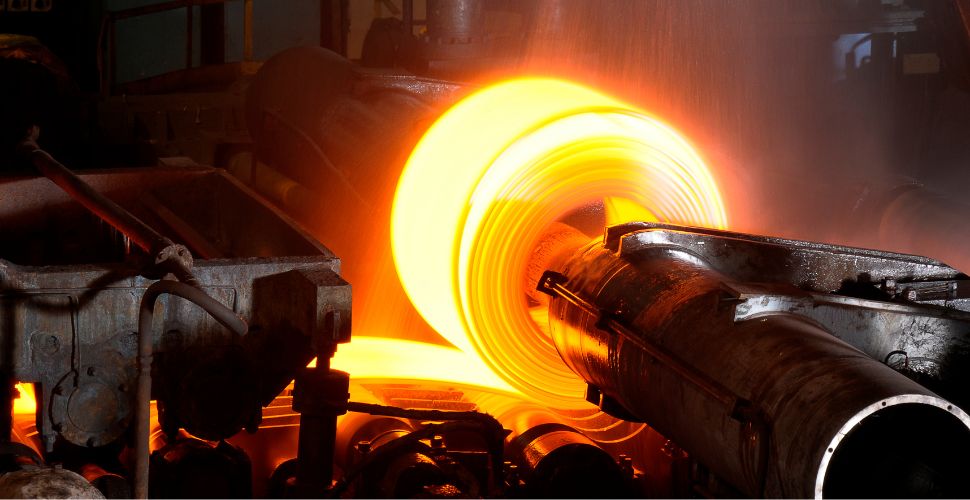

The specific objectives include the design of AI algorithms to establish efficient heating strategies, the development of Finite Element models to predict billet temperature, the creation of a virtual laboratory to generate synthetic samples, and the use of these models to optimize the manufacturing process.
Line 2: Prediction of Steel Embrittlement in Nuclear Power Plants
This line of research, focused on the energy sector, is built on LADICIM’s ongoing collaboration with international organizations such as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), and the Spanish National Research Centre for Energy, Environment and Technology (CIEMAT). These partnerships have enabled LADICIM to access the world’s most comprehensive database on the embrittlement experienced by nuclear reactor pressure vessels under operational conditions. This unique resource positions the team led by Professor Diego Ferreño to address the challenge of reactor vessel steel embrittlement—critical to the safety and longevity of fission nuclear power plants—through the development of predictive models based on machine learning.
The research aims to develop predictive models to determine the degree of embrittlement that reactor pressure vessel steels undergo as a result of neutron irradiation, with the goal of ensuring the long-term operation of fission nuclear power plants. Efforts are focused on training and validating algorithms that support the identification of safe operational conditions, the design of predictive surveillance programs, and the enhancement of structural integrity in critical nuclear components.
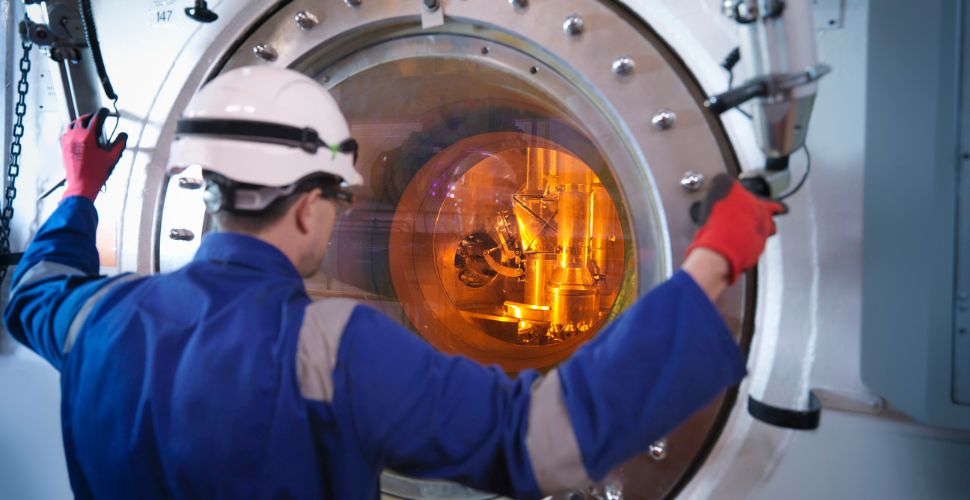

Line 3: Development of High-Performance Concretes for Offshore Wind Energy
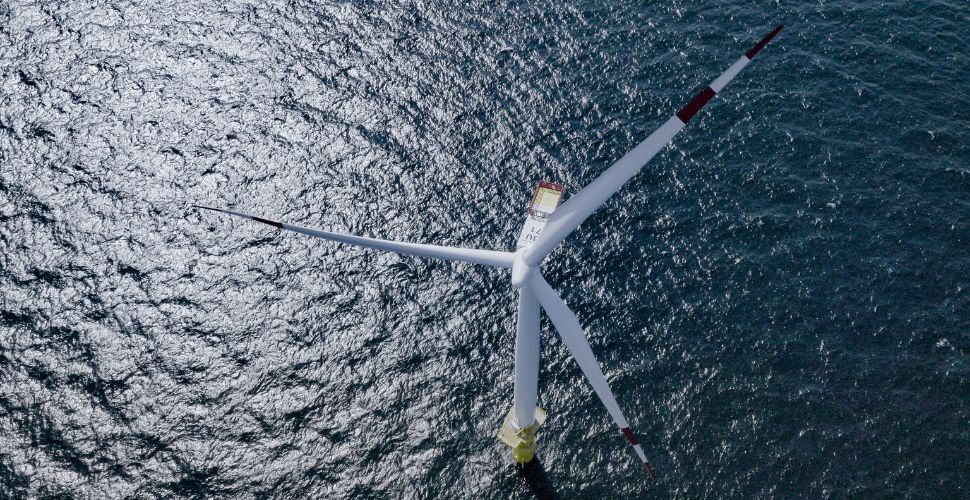
The third line of research within INTELEST focuses on developing innovative solutions for offshore wind energy generation, specifically through the construction of floating wind platforms made from concrete instead of steel. This initiative responds to the challenges posed by the harsh marine environment and the mechanical demands of wind and waves, which negatively affect the durability and efficiency of traditional steel structures.
The ongoing collaboration between LADICIM, the Environmental Hydraulics Institute (IHCantabria), and the concrete prefabrication company Rocacero highlights a shared commitment to innovating materials and construction techniques that enhance the sustainability and performance of infrastructure for renewable energy generation at sea.
This research line, led by LADICIM professor Isidro Carrascal, is dedicated to the development of high-performance concretes for use in offshore floating wind platforms. The innovation aims to replace steel with prestressed concrete to improve the durability and strength of these structures in harsh marine conditions.
The project leverages Artificial Intelligence algorithms to optimize the concrete mix design, ensuring it meets specific requirements for workability, structural integrity, and durability.

Line 4: Predictive Maintenance of High-Speed Rail Infrastructure
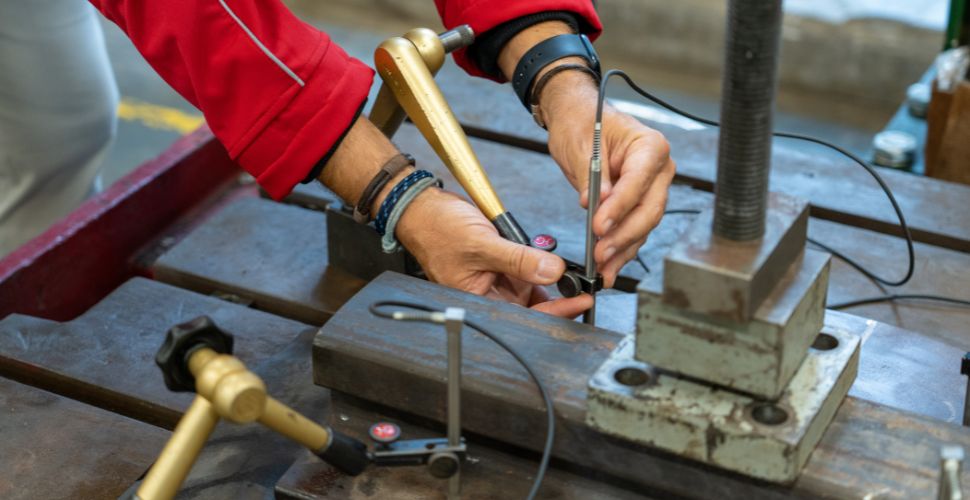
The foundation of this line of research lies in LADICIM’s extensive experience from previous collaborations focused on optimizing high-speed railway superstructure components. For over three decades, the Laboratory has carried out research aimed at improving the connectivity and sustainability of rail transport in Cantabria, working with regional, national, and international companies such as Redalsa, MAFEX, Pandrol, and the Spanish Railway Infrastructure Manager (ADIF), among others.
This line of work, led by LADICIM professor and director José A. Casado, focuses on designing tools for the predictive maintenance of high-speed rail infrastructure. These include the application of Finite Element numerical modeling and Artificial Intelligence algorithms to optimize maintenance management—shifting from a reactive or preventive approach to a predictive one.
The goal is to predict the mechanical behavior and damage progression of superstructure components—such as ballast, sleepers, and fastening systems—under operational and aging conditions. The team aims to develop a holistic model that simulates track behavior in real conditions, as well as machine learning algorithms capable of inferring the damage level of components based on inspection data. This approach will help reduce operational and maintenance costs while enhancing the safety and reliability of high-speed rail transport.

The INTELEST project, through an innovative approach that promotes knowledge transfer and the application of advanced Artificial Intelligence and numerical simulation technologies, will enhance the competitiveness of the participating companies. By optimizing processes, reducing operational and energy costs, and improving operational efficiency, the involved companies will be better positioned in the market. Furthermore, their long-term positioning will also improve thanks to the added value of adopting cutting-edge technologies and sustainable practices. These benefits are expected to extend to other companies and industrial sectors in the future.




